Eczema Vs. Psoriasis: Symptoms, Treatments & Key Differences
Eczema and psoriasis are two common skin conditions that often get confused due to their similar appearance. However, they are distinct diseases with different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management and treatment. This article delves deep into the distinguishing features of eczema and psoriasis, providing a comprehensive understanding of both conditions.
What is Eczema? Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, redness, and itching. It often appears in early childhood but can persist into adulthood.
Causes of Eczema
Eczema is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A malfunction in the skin barrier, which normally retains moisture and protects against allergens, leads to increased sensitivity and reactivity. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as eczema tends to run in families, suggesting a hereditary component. Additionally, environmental triggers such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, and harsh soaps can provoke eczema flare-ups. Stress and temperature changes can also exacerbate the condition.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema manifests in various forms, but common symptoms include dry, sensitive skin, intense itching, and red, inflamed areas. The skin becomes dry and more prone to irritation, leading to severe itching that results in scratching, which worsens the condition. Affected areas often appear red and inflamed, with rashes occurring anywhere on the body, commonly on the hands, feet, neck, and the insides of the elbows and knees. Chronic scratching can lead to thickened, leathery skin.
Treatment for Eczema
Effective management of eczema involves regular moisturizing to maintain the skin barrier, using topical steroids to reduce inflammation and itching, and avoiding known triggers. In severe cases, doctors may prescribe systemic treatments. Keeping the skin hydrated is essential, and prescription medications can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
What is Psoriasis? Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that accelerates the life cycle of skin cells. This rapid turnover leads to the buildup of cells on the skin’s surface, forming scales and red patches that can be itchy and sometimes painful.
Causes of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is primarily an autoimmune disorder, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. Genetic factors play a significant role, as psoriasis often runs in families. The overactive immune response leads to the rapid production of skin cells. Environmental triggers such as infections, stress, smoking, and certain medications can also trigger or worsen psoriasis.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
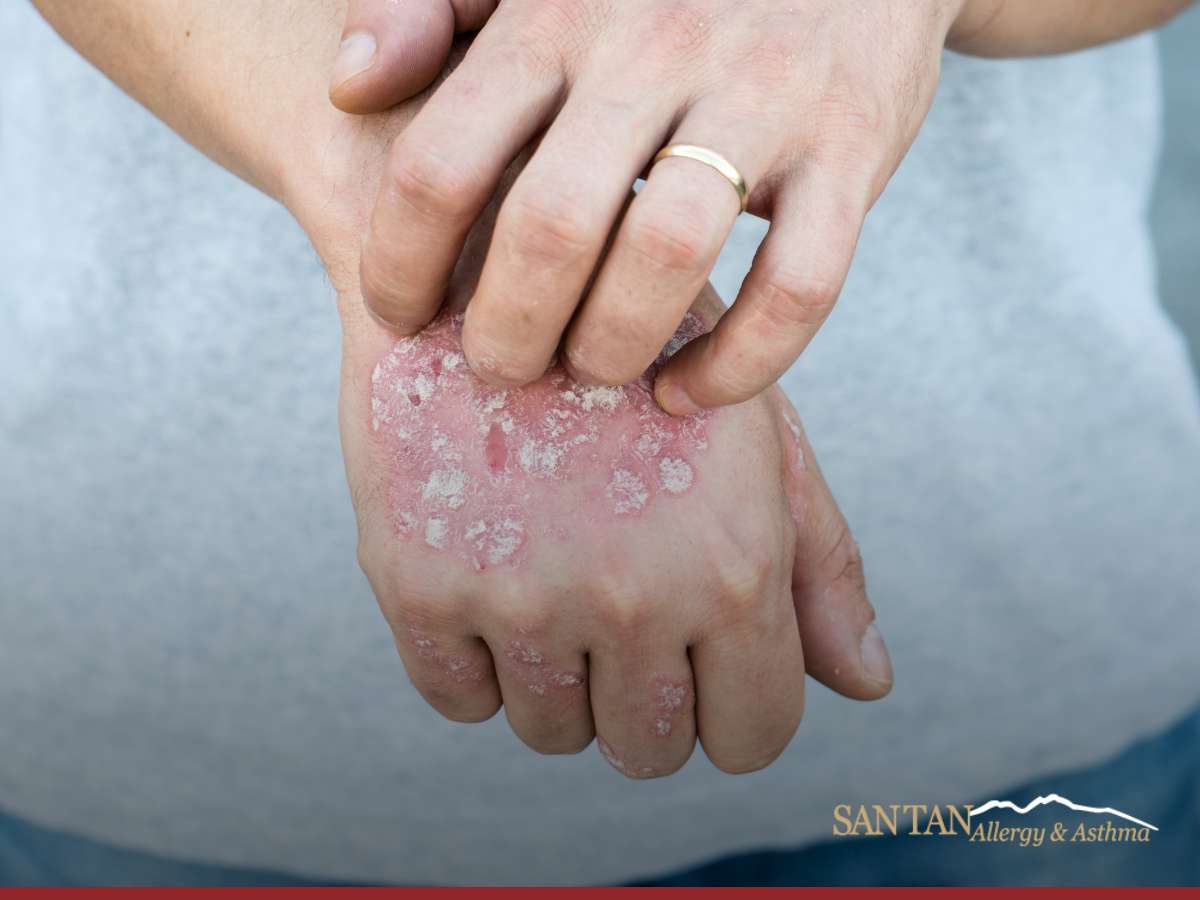
Psoriasis can present in various forms, but common symptoms include well-defined red patches with silvery scales, dry and cracked skin, itching and burning, thickened nails, and joint pain. The red patches are covered with silvery scales, and the skin is thicker in affected areas, which may crack and bleed. Itching and burning sensations are common, and the condition can also affect the nails, causing them to become thickened, pitted, or ridged. Some individuals with psoriasis also develop psoriatic arthritis, leading to joint pain and swelling.
Treatment for Psoriasis
Managing psoriasis typically involves topical treatments such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids. Phototherapy, or exposure to ultraviolet light, can help reduce symptoms. Systemic medications, which affect the entire body, are used for severe cases, and biologic drugs target specific parts of the immune system for moderate to severe psoriasis.
Key Differences Between Eczema & Psoriasis
While both conditions affect the skin and share some symptoms, several key differences help distinguish them:
- Appearance: Eczema typically appears as red, inflamed skin with intense itching, often accompanied by dry, sensitive skin that can become thick and leathery from scratching. In contrast, psoriasis presents as well-defined red patches with silvery scales, with thicker skin and affected areas that may crack and bleed.
- Location: Eczema commonly affects the flexural areas, such as the inside of the elbows, behind the knees, and on the neck and face. Psoriasis often appears on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back, and can also affect the palms, soles, and nails.
- Itchiness: Intense itching is a hallmark of eczema, leading to scratching that exacerbates the condition. Psoriasis, while it can be itchy, is more commonly associated with a burning or stinging sensation.
- Age of Onset: Eczema often begins in infancy or early childhood and can persist into adulthood, while psoriasis typically develops in early adulthood but can occur at any age.
Eczema & Psoriasis: Links to Allergy & Asthma Conditions
Both eczema and psoriasis have connections to other allergic conditions, but these associations differ. Eczema is commonly linked with other atopic conditions such as asthma and hay fever. Individuals with eczema often have a history of allergies and may benefit from seeing an allergy doctor for comprehensive care. On the other hand, psoriasis is less commonly associated with allergic conditions, but individuals with psoriasis may still experience comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease or metabolic syndrome.
Diagnosis & Testing
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Allergy tests and consultations with an allergist can be beneficial for those with eczema, particularly when identifying triggers. Asthma testing may also be relevant for individuals with concurrent respiratory issues. Dermatologists examine the skin’s appearance and distribution of lesions, and a skin biopsy may be performed to distinguish between eczema and psoriasis.
Treatment Approaches for Eczema & Psoriasis
The treatment strategies for eczema and psoriasis differ due to their distinct pathophysiologies:
Eczema Treatment
Eczema treatment involves regular use of moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated, topical steroids to reduce inflammation and itching, and immunomodulators to help regulate the immune response. Antihistamines can provide relief from itching, and avoiding known triggers is crucial for preventing flare-ups.
Psoriasis Treatment
Topical treatments for psoriasis include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids. Phototherapy, which involves exposure to UV light under medical supervision, can help reduce symptoms. Systemic medications, which target the entire body, are used for severe cases, and biologic drugs offer advanced treatments by targeting specific parts of the immune system.
Your Best Choice for Comprehensive Skin & Allergy Care
Eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. Effective management requires accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan from specialists. Trust the experts at San Tan Allergy & Asthma to provide personalized care for eczema, psoriasis, and related conditions. Let us help you achieve better health and well-being. Contact us today!
San Tan Allergy & Asthma
4915 E Baseline Rd #112
Gilbert, AZ 85234
Phone: 480-626-6600
Email: officemanager@santanallergy.com
Website: https://santanallergy.com/